Every successful product you see around you started with a spark of an idea. But how does that concept change into something you can touch, use, or encounter? The product development process holds the key. An organized road map from idea to reality, this technique helps to lower risks and fit with market needs.
Knowing the product development process is vital in the cutthroat arena of invention. For any product development company, particularly those providing product design services and prototype manufacturing, this process constitutes the core of their work.
1. Idea Generation: Laying the Foundation
Ideation defines the initial stage of the product development process. This is not only arbitrary brainstorming. It includes studying consumer demands, tracking trends, looking at market gaps, and gathering internal team insights.
Often, a good idea emerges from spotting an issue that individuals wish to fix. Many wearable technology developments, for instance, came from the basic desire for real-time health monitoring. At this point, product design services assist in visualizing first ideas and drawings.
In Shenzhen, where innovation is ingrained in the culture, access to advanced technology and talented engineers often drives idea generation. This atmosphere is perfect for new product concepts to thrive since it speeds innovation.
2. Idea Screening: Filtering the Noise
Once several ideas are on the table, it is time to assess which ones are truly worth chasing. The product development process depends much on idea screening since it conserves time, money, and effort. Companies now evaluate technological viability, market need, and return on investment.
Reviewing ideas involves internal stakeholders, including teams from product development agencies. Ideas with little commercial potential or those that conflict with fundamental corporate objectives are rejected. Early pivoting is preferable to investing in a dead-end.
3. Concept Development and Testing: Building on a Strong Idea
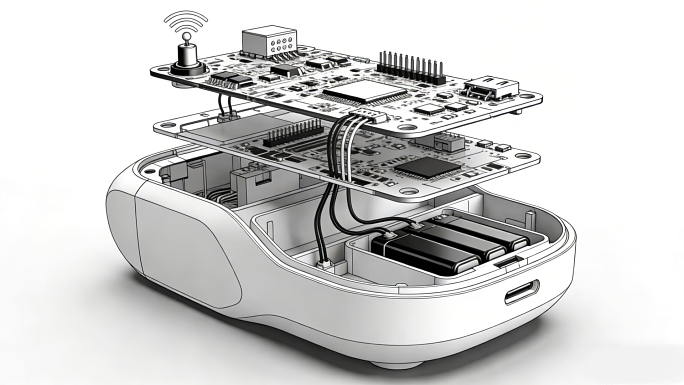
The product concept now gets developed in detail with a selected promising notion. Designers and engineers here build low-fidelity prototypes, wireframes, and visual mockups. These assist in picturing the shape, use, and user experience of the product.
Testing by users starts early. Target consumers are frequently used in concept testing to confirm whether the product speaks to their requirements. Prototype manufacturing takes center stage in the product development process at this point. Prototypes let teams validate hypotheses, collect comments, and improve the design before significant expenditures.
4. Business Analysis: Weighing the Numbers
Business study comes next when concept validation is favorable. Strategy meets practicality at this step of the product development process. Teams determine income models, forecast demand, and compute development expenses. How much will it cost to construct? Is it scalable? What are the hazards?
Product development companies have to take into account not just the price of materials and labor but also transportation, packaging, and legal approvals. This study usually involves looking at collaborations with manufacturers in Shenzhen, where supply chain access is extensive.
Recent industry studies show that around 45% of new product failures are caused by inadequate market research. This emphasizes the importance of this stage.
5. Product Development: Engineering the Solution
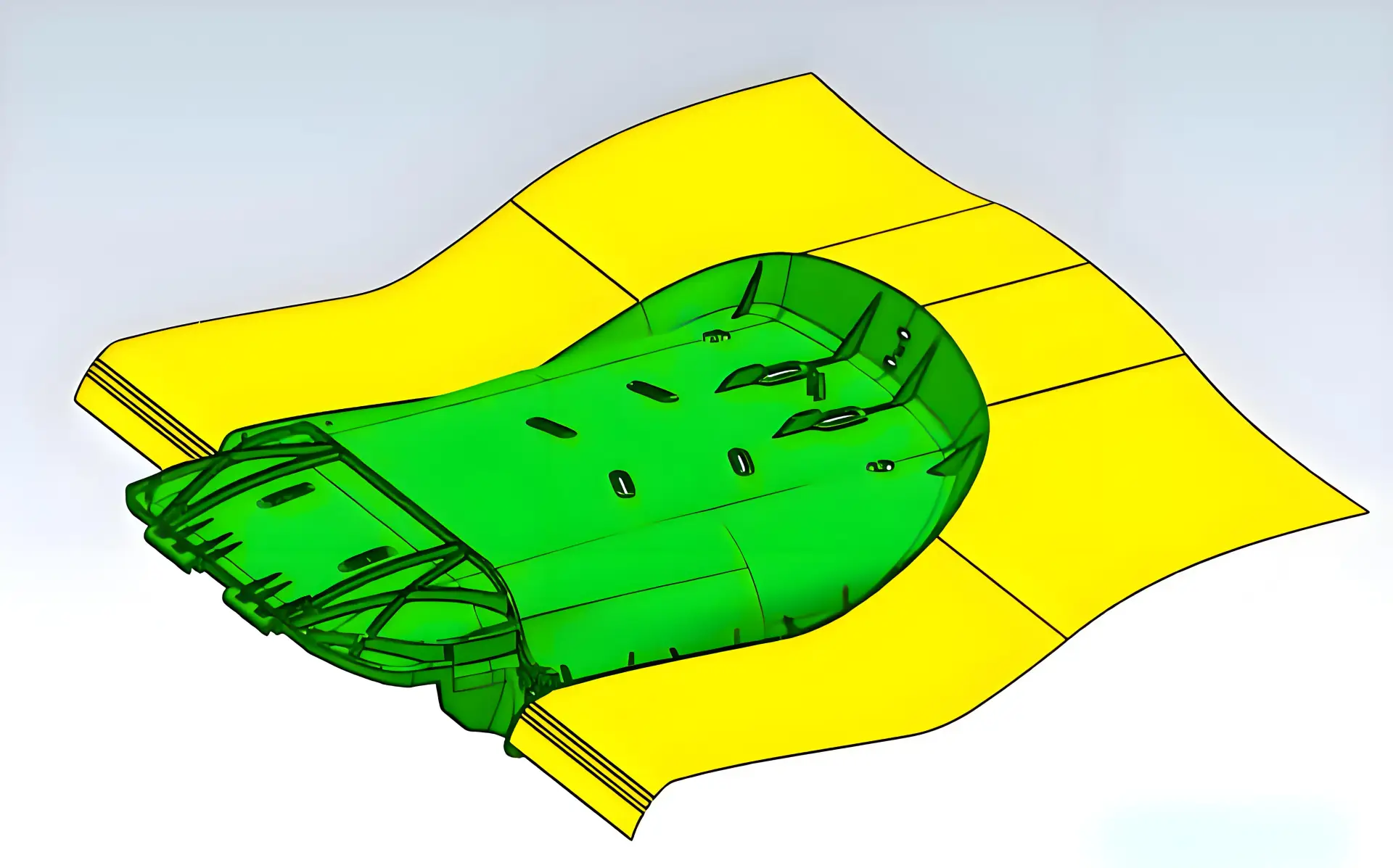
The product’s actual creation starts now. Working together, engineers, industrial designers, and developers turn the approved idea into a practical product. Establishing technical specifications, developing CAD models, and improving the MVP define this stage of the product development process.
Now, product design services concentrate on compliance and manufacturability. From material selection to ergonomics, everything is maximized. Prototype manufacturing and mold creation take front stage for tangible objects. Especially in hardware design, teams could cycle through many prototype iterations before deciding on a final version.
The aim is to design a product that is reasonably priced to manufacture at scale and also useful.
6. Testing and Validation: Polishing the Product
The product has to be evaluated exhaustively before it goes on sale. This calls for outside beta testing as well as internal testing. All are assessed: usability, lifetime, safety, and user happiness. Testing is about making sure the product is wanted as well as about identifying flaws.
This stage of the product development process lets teams finalize changes depending on actual input. Often, product development companies employ consumer data to improve packaging, design, and directions. Electronics need compliance certificates like CE, FCC, and RoHS.
A recent survey revealed that about 63% of consumers give up on new items because of usability issues, therefore highlighting the need for this phase.
7. Market Launch: Introducing the Product
Once confirmed, the product is set to greet the globe. The product development process depends on launch planning. Product marketing groups set go-to-market plans, positioning, and messaging. The aim is to draw early adopters, create comments, and build momentum.
Whether starting a digital service or physical product, marketing, design, and sales must all work in concert. The strategic position in Shenzhen allows quicker distribution and shorter shipping times, therefore enabling enterprises to be competitive.
Feedback after launch is gathered constantly and applied to enhance next versions or spot the need for version changes.
8. Post-Launch Support and Iteration
Launch doesn’t finish the product development cycle. Post-launch monitoring reveals chances for improvements, user issues, and defects. Development teams keep working on fresh features, upgrades, or perhaps supplementary items.
During this time, product development companies keep long-term client connections. Included in support are cost-reduction plans, supply chain optimization, warranty administration, and production scaling. The knowledge from this stage informs the concept generation process for the following product cycle.
Why the Product Development Process Matters
A well-organized product development approach helps to lower the likelihood of expensive mistakes. It enables improved risk management, budget control, and planning. Following this approach helps to clarify and streamline the road to market whether the company is a startup or an enterprise.
Fundamentally, this approach is about teamwork. It brings together technical specialists, analytical thinkers, and creative brains to develop something meaningful. When handled correctly, it results in greater company results, happier consumers, and stronger products.
Conclusion
Any company trying to create with confidence must first grasp the product development process. Every stage from the first idea to a completely launched product has a goal and reduces risk. This approach is supercharged in China’s innovation centers, such as Shenzhen, where talent and technology meet.
A trustworthy product development company uses this approach to provide quicker releases, improved outcomes, and cheaper prices. For businesses wishing to realize their concepts, this path is not only required but also life-changing.