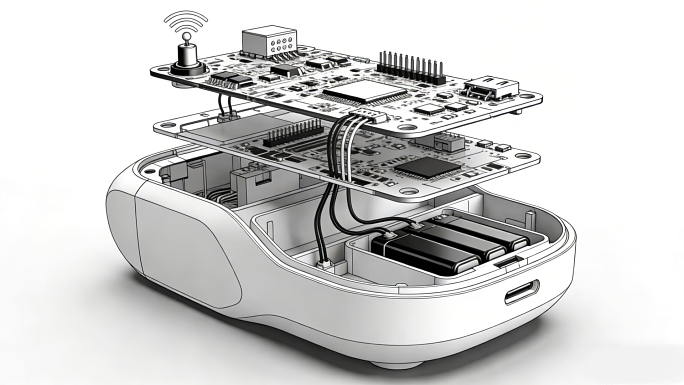
Behind every physical item used in daily life lies a process few people consider. This method makes a concept actual, tangible, and ready for the market. The mechanical design engineer is the core of this approach. Mechanical design engineers are essential in translating ideas into the real world, from developing home products’ inner workings to improving industrial gears’ construction.
This article investigates their significance, interaction with other fields, and the step-by-step process that transforms ideas into reality.
What Does a Mechanical Design Engineer Do?
A mechanical design engineer designs, improves, and verifies the mechanical systems enabling product operation. Whether it’s a basic hinge or a sophisticated robotic arm, their responsibility is to ensure that every component operates securely and harmoniously. They create components satisfying technical and user needs using engineering concepts, material science, and production expertise.
Mechanical design engineers are engaged from the early phases of development. Working with product design engineers, industrial designers, and product managers, they transform abstract ideas into practical designs. Their aim is to create affordable, manufacturable, practical solutions. Their function in product development is crucial because of this balance of inventiveness and pragmatism.
The Collaboration Between Industrial Design and Mechanical Engineering
Product development is seldom the labor of one specialist. Instead, it’s a joint effort combining industrial design and mechanical design engineering. Industrial design emphasizes the product’s emotional appeal, user experience, and look. Conversely, mechanical design engineers ensure the item works as planned and withstands actual use.
A mechanical design engineer determines how to fit all the internal parts without sacrificing the design, even if an industrial designer envisions a slick outside for a new product. Design studios, manufacturers, and industrial design centers worldwide host this cooperation.
Shenzhen, China, for instance, is home to several businesses where this cooperation flourishes. These industrial centers unite design and manufacturing professionals to speed product development, giving access to manufacturers, suppliers, and engineers.
From Concept to Blueprint: The Design Engineer’s Process
A concept starts the path. Whether motivated by a commercial necessity or an inventive idea, this notion is the seed that mechanical design engineers assist in cultivating into reality. Possible mechanical solutions are initially brainstormed. Engineers concentrate on spotting problems, technical needs, and user expectations throughout this stage.
After selecting a viable idea, the design engineer produces the first sketches and basic models. These depictions highlight the fundamental structure and use. At this point, industrial designers and product design engineers work together to ensure the item satisfies practical and aesthetic objectives.
The mechanical design engineer converts these crude concepts into thorough blueprints using techniques, including Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. These computer models provide motion research, stress assessments, and virtual simulations. Industry statistics show that businesses that spend money on simulation tools and CAD experience up to 30% fewer design changes later in the process. This not only cuts development expenses but also saves time.
Prototyping and Real-World Testing
Prototyping follows the completion of the digital model. A prototype is a physical representation of the design created to evaluate and confirm its performance. This is when the mechanical design engineer’s labor truly comes to life. Prototypes let engineers observe how the components interact, move, and respond to stress or contact.
Prototyping is seldom a one-time activity. Often, several iterations are required. Every edition points out areas needing work. Mechanical design experts employ this practical testing to hone their designs. Real-world testing offers insights that digital simulations cannot completely convey. Teams identify possible problems during this phase before going to mass manufacture.
Statistics indicate that businesses adopting 3D printing and other fast prototype techniques can save as much as 50% of development time. This speed benefit lets companies guarantee quality criteria for their products and help them reach the market quicker.
Validating Functionality and Safety
If the prototype runs as anticipated, mechanical design engineers proceed to testing for dependability and safety. This stage involves putting the product through several situations to ensure it satisfies all performance and regulatory criteria. Engineers might perform mechanical stress tests, heat analysis, and drop tests.
This stage keeps product design engineers working with industrial design teams and product design engineers. The item must work well and satisfy the user’s expectations for longevity and usage. A mechanical design engineer has to confirm that the product will operate consistently under actual circumstances.
Preparing for Production
With a confirmed design, the mechanical design engineer turns attention to manufacturing readiness. This stage calls for cooperation with producers to guarantee the design can be mass-produced. The engineer offers thorough assembly instructions, material lists, and specs.
A key component of this procedure is cost control. Mechanical engineers must maximize the design to minimize material waste, lower assembly time, and guarantee quality control. They obtain the appropriate materials and components by working directly with supply chain teams.
Manufacturing centers like Shenzhen benefit from this stage’s proximity to production sites. Engineers swiftly fix any problems that arise during pilot production runs. Companies participating actively like this can lower the hazards of expanding to complete manufacturing.
Solving Real-World Challenges with Engineering Expertise
Mechanical design engineers face difficulties at every development level. From financial limits to technical challenges, problem-solving is crucial to their work. They seek answers using technical concepts and hands-on knowledge that balance performance, cost, and manufacturability.
A product, for instance, could need a certain material for durability, yet that material could be too pricey or hard to obtain. The mechanical design engineer has to locate a substitute that satisfies performance criteria without exceeding the budget. This balancing act makes their job difficult and important.
The capacity to negotiate these obstacles not only determines the product’s performance but also influences the reputation and profitability of the business. Business success depends on engineers who provide on-time, within-budget, dependable, high-quality products.
The Growing Importance of Mechanical Design Engineering
The function of the mechanical design engineer becomes more vital as sectors change. Technological developments, including intelligent manufacturing systems and AI-driven design tools, alter how goods are created. To stay competitive, mechanical design engineers must keep up with innovations.
They are also more engaged in projects for sustainable design. Mechanical design engineers lessen the environmental effect of products by choosing sustainable materials and optimizing manufacturing processes. This movement toward sustainability is a market expectation, not only a trend. Surveys reveal that 72% of customers consider sustainability while selecting items.
Mechanical design engineering’s future will require increasingly more cooperation among industrial design, product design engineers, and production specialists. Businesses that support this cross-disciplinary cooperation will be better able to create and compete in the world market.
Conclusion
Mechanical design engineers connect ideas to reality. They turn concepts into practical, manufacturable goods satisfying consumer expectations and market needs. Working with industrial design and product design engineers helps them guarantee that items appear well and function consistently. Every stage in the process, from digital modeling to real-world testing, depends on their knowledge.
Their function is more crucial than ever in today’s fast-paced, competitive markets. Businesses that spend money on qualified mechanical design engineers will be better able to create creative goods, satisfy consumer needs, and have long-term success.