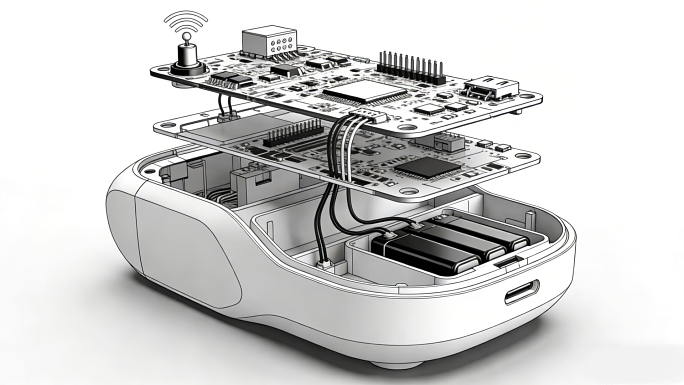
Product design and product engineering are two closely connected disciplines that play different but equally important roles in bringing a product to market. While they are often grouped together, understanding how they differ—and how mechanical design connects them—helps businesses make better development decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
At OPD Design, structured product development services integrate product design, mechanical engineering, strategy, and prototyping into one seamless workflow. This ensures ideas move efficiently from concept to production while remaining user-focused, technically sound, and commercially viable.
This blog explains the difference between product design and product engineering, highlights the role of mechanical design, and shows how an integrated approach leads to better products.
What Is Product Design?
Product design focuses on defining the product from a user, market, and business perspective. It begins by identifying user needs, understanding problems, and shaping solutions that deliver value. The goal of product design is to create products that are intuitive, functional, and aligned with real-world use.
During this phase, designers explore form, usability, ergonomics, and interaction. Concept sketches, digital models, and early validation help refine ideas before technical development begins. Strong product design reduces uncertainty and provides a clear direction for engineering teams.
Product Design and User Experience
A key aspect of product design is user experience. Designers evaluate how users interact with the product, how easily it can be understood, and how comfortable it is to use. By focusing on usability early, product design helps prevent issues that could negatively affect adoption or satisfaction later.
Iteration in Product Design
Iteration is a core principle of product design. Designers refine concepts through repeated testing, prototyping, and feedback. This process ensures that the product evolves to meet user expectations while remaining feasible for engineering and production.
What Is Product Engineering?
Product engineering takes product design concepts and turns them into working, manufacturable solutions. It focuses on feasibility, performance, reliability, and compliance with technical requirements.
Engineers analyze materials, tolerances, loads, and assembly methods to ensure the product can be produced consistently and perform as expected. Product engineering ensures that design ideas are not only creative but also practical and scalable.
Engineering for Reliability and Compliance
Product engineering ensures products meet performance expectations, safety standards, and regulatory requirements. This step is essential for delivering solutions that perform reliably throughout their lifecycle and across different operating conditions.
Product Design vs Product Engineering: Key Differences
The main difference lies in intent and execution. Product design focuses on the user experience and overall concept, while product engineering focuses on technical performance and buildability.
Product design defines what the product should be and how it should feel. Product engineering defines how it will work and how it will be made. Mechanical design bridges this gap by converting design intent into engineered systems that meet functional and manufacturing requirements.
Without alignment between these disciplines, products often face delays, redesigns, or increased development costs.
The Role of Mechanical Design in Product Development
Mechanical design plays a central role throughout the development process. It transforms product design concepts into detailed mechanical systems that can be manufactured and assembled.
Mechanical designers create CAD models, define component relationships, select materials, and specify tolerances. These decisions directly affect performance, durability, cost, and production efficiency.
Mechanical Design and Manufacturing Readiness
A common challenge in product development is designing products that look good but are difficult to manufacture. Mechanical design addresses this by considering manufacturing processes early in the project.
By evaluating methods such as injection molding, machining, or sheet metal fabrication from the start, mechanical designers reduce production risks and prevent late-stage changes. This approach shortens development cycles and improves cost control.
Performance-Focused Mechanical Design
Mechanical design also ensures that products meet strength, thermal, and efficiency requirements. Through simulation and analysis, components are optimized for durability and material efficiency, ensuring that the final product performs reliably in real-world conditions.
How Product Strategy Services Guide Better Decisions
Before design and engineering begin, product strategy services help define direction. Product strategy aligns business goals, customer needs, and technical capabilities to ensure the right product is being built.
A clear strategy guides product design priorities and helps engineering teams focus on features that matter most. Mechanical design then supports this strategy by delivering solutions that balance performance, cost, and scalability.
Strong product strategy reduces risk and ensures development efforts support long-term business success.
Product Prototyping Services and Validation
Product prototyping services allow teams to test and refine designs before committing to full production. Prototypes help validate form, fit, and function while revealing potential issues early.
Mechanical design is essential during prototyping. Accurate models ensure prototypes behave like final products. Testing results feed back into design improvements, strengthening both product design and engineering outcomes.
Reducing Risk Through Early Testing
Early-stage prototyping identifies design and engineering challenges before they impact timelines or budgets. Functional testing and mechanical validation increase confidence and reduce uncertainty prior to production investment.
Collaboration Between Design and Engineering Teams
Successful product development depends on collaboration. Product designers and engineers must work together throughout the process to avoid misalignment.
Mechanical design acts as a shared reference point, connecting visual intent with technical execution. Clear documentation and regular communication reduce rework and speed up development.
Integrated product development services support this collaboration by keeping teams aligned from start to finish.
Avoiding Common Product Development Challenges
When product design and engineering operate separately, problems often arise. Designs may be visually appealing but impractical, or technically sound but difficult to use.
Mechanical design helps balance aesthetics, function, and feasibility. Early involvement ensures potential issues are resolved before they affect schedules or costs.
Iteration and Scalability in Product Development
Iteration is a key principle of product design. Feedback from prototyping, testing, and engineering analysis drives continuous improvement.
Mechanical design supports iteration by enabling fast updates to models and assemblies. At the same time, it considers tooling, assembly efficiency, and supply chain factors to ensure products can scale as demand grows.
Why Integrated Product Development Services Matter
Integrated product development services bring product design, engineering, strategy, and prototyping into one coordinated process. This reduces handoffs, improves accountability, and accelerates time to market.
Mechanical design benefits from this integration by staying connected to both creative and technical inputs. The result is a product that meets user needs, engineering standards, and business goals.
Final Thoughts: Aligning Product Design and Engineering
Product design and product engineering are distinct but deeply connected. Mechanical design bridges the gap by translating ideas into buildable, scalable solutions. If you are planning a new product or refining an existing concept, contact us to discuss your goals and technical requirements.
By combining strong product design, structured engineering, and integrated product development services, businesses can move confidently from concept to production. Supported by product strategy services and validated through product prototyping services, this approach delivers products that are practical, user-focused, and ready for market success.
FAQs
1. What is the main purpose of product design in development?
Product design focuses on creating user-centered solutions that balance functionality, usability, and visual appeal.
2. How does mechanical design fit into product engineering?
Mechanical design translates product design concepts into technical systems that are strong, reliable, and ready for manufacturing.
3. Why are product strategy services important before design begins?
Product strategy services help define user needs, market opportunities, and business objectives, guiding effective design decisions
4. How do product prototyping services support the design process?
They allow teams to test form, function, and performance, reducing risks before full-scale production.
5. Can a single partner manage product design and engineering together?
Yes, integrated services ensure better coordination, faster timelines, and consistent product outcomes.






